
This is similar to the effect of velvet fabric over a convex curved surface which to an observer will appear darkest at the center of the curve.
PICTURE OF LUNAR ECLIPSE DIAGRAM FULL
This is because as viewed from the Earth, the brightness of a lunar limb is generally greater than that of the rest of the surface due to reflections from the many surface irregularities within the limb: sunlight striking these irregularities is always reflected back in greater quantities than that striking more central parts, and is why the edges of full moons generally appear brighter than the rest of the lunar surface. Later, as the Moon's opposite limb is struck by sunlight, the overall disk will again become obscured. The moment the Moon enters a complete eclipse, the entire surface will become more or less uniformly bright.

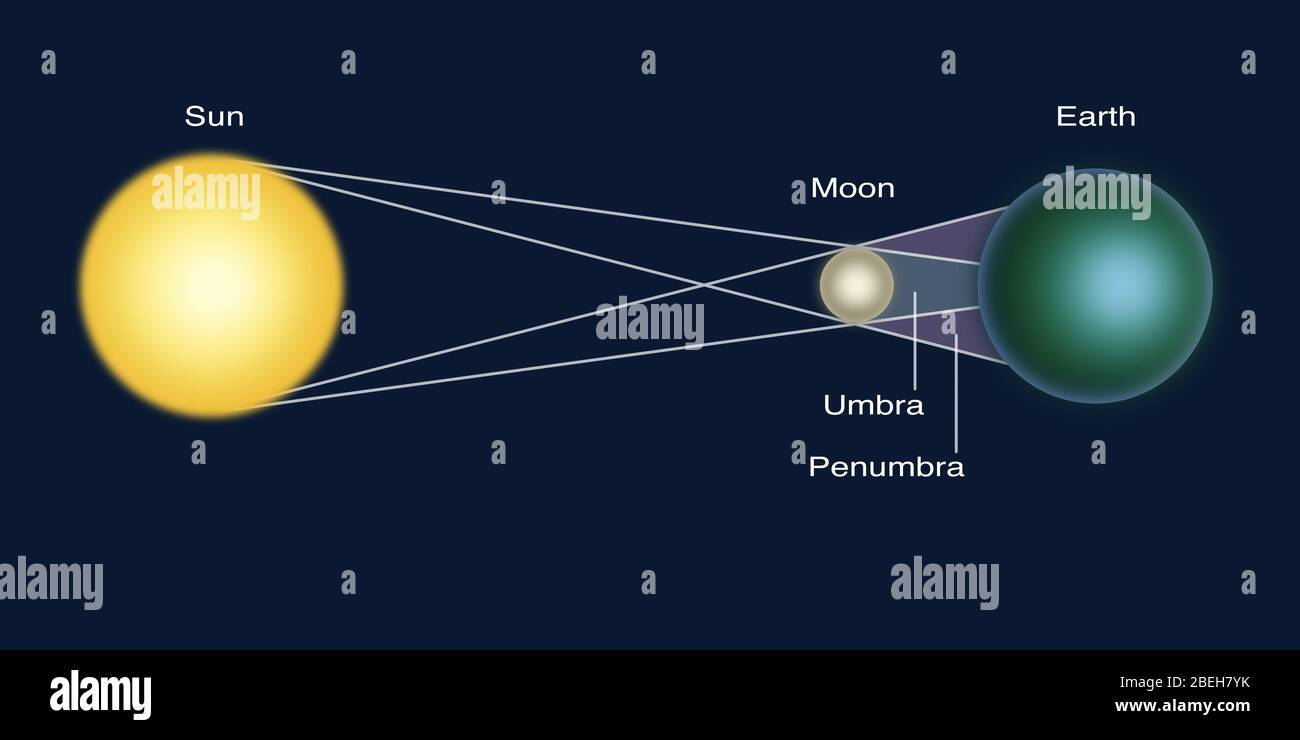
Just prior to complete entry, the brightness of the lunar limb-the curved edge of the Moon still being hit by direct sunlight-will cause the rest of the Moon to appear comparatively dim. If the Moon entirely passes into the Earth's umbra, a total lunar eclipse occurs. Nevertheless, the total time between the first and the last contacts of the Moon's limb with Earth's shadow is much longer and could last up to 236 minutes. The Moon's average orbital speed is about 1.03 km/s (2,300 mph), or a little more than its diameter per hour, so totality may last up to nearly 107 minutes. When the Moon penetrates partially into the Earth's umbra, it is known as a partial lunar eclipse, while a total lunar eclipse occurs when the entire Moon enters the planet's umbra. Total penumbral eclipses are rare, and when these occur, the portion of the Moon closest to the umbra may appear slightly darker than the rest of the lunar disk. A special type of penumbral eclipse is a total penumbral lunar eclipse, during which the Moon lies exclusively within Earth's penumbra. The penumbra causes a subtle dimming of the lunar surface, which is only visible to the naked eye when about 70% of the Moon's diameter has immersed into Earth's penumbra. However, since the Sun's diameter appears about one-quarter of Earth's in the lunar sky, the planet only partially blocks direct sunlight within the penumbra, the outer portion of the shadow.Ī penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes only into the Earth's penumbra. Earth totally occludes direct solar radiation within the umbra, the central region of the shadow. (Neither the Sun, Moon, and Earth sizes nor the distances between the bodies are to scale.)Įarth's shadow can be divided into two distinctive parts: the umbra and penumbra. In contrast, within the penumbra, the outer portion, the sunlight is only partially blocked. Within the umbra, the central region, the planet totally shields direct sunlight. The symbol for a lunar eclipse (or indeed any body in the shadow of another) is (U+1F776 🝶).Ī schematic diagram of the shadow cast by Earth. Also unlike solar eclipses, lunar eclipses are safe to view without any eye protection or special precautions. A total lunar eclipse can last up to nearly 2 hours, while a total solar eclipse lasts only up to a few minutes at any given place, because the Moon's shadow is smaller. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. This light appears reddish due to the Rayleigh scattering of blue light, the same reason sunrise and sunsets are more orange than during the day. When the moon is totally eclipsed by the Earth, it takes on a reddish color that is caused by the planet when it completely blocks direct sunlight from reaching the Moon surface, as only the light reflected from the lunar surface has been refracted by Earth's atmosphere. The type and length of a lunar eclipse depend on the Moon's proximity to the lunar node.


This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are exactly or very closely aligned (in syzygy) with Earth between the other two, which can happen only on the night of a full moon when the Moon is near either lunar node. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth's orbit. Latter phases of the partial lunar eclipse on 17 July 2019 taken from Gloucestershire, United KingdomĪ lunar eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the moon to be darkened.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
